
Global Aocket Introduction: A Travel Essential Guide!
Share
The importance of power sockets:
Power sockets may be one of the most overlooked details during travel, but they are closely related to our electrical equipment. There may be differences in the type, voltage, and frequency of power sockets in different countries, and the use of mismatched sockets may lead to electrical damage and even safety hazards. Therefore, understanding the importance of power sockets is the key to ensuring a smooth journey for you.Classification of socket types:
The International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) has developed a set of socket type classification standards to identify socket types in different countries and regions. These standards are classified based on features such as plug shape, number of holes, and size. Let's learn about some common socket types together.

Type A
- mainly used in the USA, Canada, Mexico & Japan
- 2 pins
- not grounded
- 15 A
- almost always 100 – 127 V
- socket compatible with plug type A

Type B
- mainly used in the USA, Canada & Mexico
- 3 pins
- grounded
- 15 A
- almost always 100 – 127 V
- socket compatible with plug types A & B

Type C
- commonly used in Europe, South America & Asia
- 2 pins
- not grounded
- 2.5 A, 10 A & 16 A
- almost always 220 – 240 V
- socket compatible with plug type C

Type D
- mainly used in India
- 3 pins
- grounded
- 6 A
- 220 – 240 V
- socket compatible with plug type D (partial and unsafe compatibility with C, E & F)

Type E
- primarily used in France, Belgium, Poland, Slovakia & Czechia
- 2 pins
- grounded
- 16 A
- 220 – 240 V
- socket compatible with plug types C, E & F

Type F
- used almost everywhere in Europe & Russia, except for the UK & Ireland
- 2 pins
- grounded
- 16 A
- 220 – 240 V
- socket compatible with plug types C, E & F
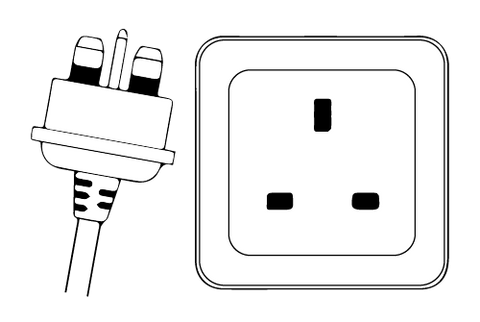
Type G
- mainly used in the United Kingdom, Ireland, Malta, Singapore & the Arabian Peninsula
- 3 pins
- grounded
- 13 A
- 220 – 250 V
- socket compatible with plug type G

Type H
- used exclusively in Israel, the West Bank & the Gaza Strip
- 3 pins
- grounded
- 16 A
- 220 – 240 V
- socket compatible with plug types C & H (partial and unsafe compatibility with E & F)

Type I
- mainly used in Australia, New Zealand, China & Argentina
- 2 or 3 pins
- 2 pins: not grounded / 3 pins: grounded
- 10 A
- 220 – 240 V
- socket compatible with plug type I

Type J
- used almost exclusively in Switzerland & Liechtenstein
- 3 pins
- grounded
- 10 A
- 220 – 240 V
- socket compatible with plug types C & J

Type K
- used almost exclusively in Denmark & Greenland
- 3 pins
- grounded
- 16 A
- 220 – 240 V
- socket compatible with plug types C & K (partial and unsafe compatibility with E & F)

Type L
- used almost exclusively in Italy & Chile
- 3 pins
- grounded
- 10 A & 16 A
- 220 – 240 V
- 10 A socket compatible with plug types C & L (10 A version)
- 16 A socket compatible with plug type L (16 A version)

Type M
- mainly used in South Africa
- 3 pins
- grounded
- 16 A
- 220 – 240 V
- socket compatible with plug type M

Type N
- used in Brazil and South Africa
- 3 pins
- grounded
- 10 A, 16 A & 20 A
- 100 – 240 V
- socket compatible with plug types C & N

Type O
- used exclusively in Thailand
- 3 pins
- grounded
- 16 A
- 220 – 240 V
- socket compatible with plug types C & O (partial and unsafe compatibility with E & F)
Wide voltage and single voltage devices:
In international travel, you not only need to consider plugs and sockets, but also single voltage and dual voltage.
Wide voltage equipment:
Wide voltage devices refer to devices that can operate normally within different voltage ranges. These devices typically have power adapters or power inputs labeled as "100-240V". Wide voltage devices can adapt to the voltage standards of different countries and regions, so you only need one adapter plug to use them.
Single voltage equipment:
Single voltage equipment refers to equipment that can only operate normally within a specific voltage range. These devices typically have power adapters or power inputs labeled as fixed voltages (such as "110V" or "220V"). If you want to use a single voltage device for countries or regions with different voltage standards, you need a transformer to adjust the voltage to match the voltage of the target ground.
How to identify whether my electrical appliance is wide voltage or low voltage:
1. Check the power adapter or power input label: Check the label on the power adapter or power input of your appliance to find information about the voltage range. Wide voltage devices are usually labeled as "100-240V", which means they can operate normally in the range of 100 to 240 volts. Single voltage devices are usually labeled as fixed voltage, such as "110V" or "220V".
2. Check the product manual or specification manual: If you have a product manual or specification manual for an electrical appliance, you can check the voltage information in it. The manual usually provides the input voltage range or specific voltage requirements for the electrical appliance.
3. Online search: If you can't find the label or manual of the appliance, you can try to search the specification of the appliance on the manufacturer's official website. Information about voltage can usually be found on the product page or in the Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) section.
4. Consult the manufacturer or after-sales support: If you are still unsure of the voltage type of the electrical appliance, it is best to directly contact the manufacturer or after-sales support team. They can provide you with accurate information and answer your questions.
Please note that if your appliance is a single voltage device and you plan to use it in countries or regions with different voltage standards, you may need to consider using a transformer to adjust the voltage to ensure that the appliance works properly and avoid damage.
Essential travel guide:
1. Understand the type of socket at the destination in advance and purchase a travel converters.
2. Carry a multifunctional charger to charge multiple devices simultaneously.
3. Back up important electronic devices to the cloud to prevent data loss.
4. Before traveling, check if your electrical equipment supports the voltage and frequency of the destination.
5. If you are staying at a hotel, inquire with the front desk about the type of socket or whether an adapter is provided.
